what statement is correct for keto enol tautomerism Keto-enol tautomerism: definition, examples, and mechanism
When it comes to organic chemistry, there are a lot of terms and concepts that can leave students scratching their heads. One such concept is keto-enol tautomerism, which refers to the interconversion of two compounds called keto and enol. This may sound like a complex topic, but we’re here to break it down for you. First, let’s define the terms keto and enol. A keto compound is one that contains a carbonyl group (C=O), while an enol is a compound that contains both an alkene group (C=C) and a hydroxyl group (OH). The two forms are in equilibrium and can rapidly interconvert in solution. So, what is keto-enol tautomerism? It’s simply the process of interconversion between the keto and enol forms of a compound. This process involves the shifting of a hydrogen atom and some electron density between the carbonyl and alkene groups, resulting in the formation of the other form. Now, you may be wondering why this is an important concept to understand. Well, keto-enol tautomerism is actually involved in many chemical reactions, including some that are essential to the functioning of our bodies. For example, the interconversion of glucose and fructose in the body occurs via a keto-enol tautomerism reaction. Let’s take a look at some examples of keto-enol tautomerism in action. One example is the interconversion of cyclohexanone and cyclohexene-1-ol. In the keto form, cyclohexanone has a carbonyl group, while in the enol form, cyclohexene-1-ol has both an alkene group and a hydroxyl group. To represent this interconversion in an engaging way, here’s what it would look like in HTML format:
When we look at the conversion of cyclohexanone to cyclohexene-1-ol, we see an example of keto-enol tautomerism in action. Here’s how it happens:
Keto Form: Cyclohexanone
 In the keto form, cyclohexanone contains a carbonyl group, which is highlighted in red.
In the keto form, cyclohexanone contains a carbonyl group, which is highlighted in red.
Enol Form: Cyclohexene-1-ol
 In the enol form, cyclohexene-1-ol contains both an alkene group (highlighted in red) and a hydroxyl group (highlighted in blue).
In the enol form, cyclohexene-1-ol contains both an alkene group (highlighted in red) and a hydroxyl group (highlighted in blue).
As you can see, the interconversion between these two forms involves the shifting of a hydrogen atom and some electron density, resulting in the formation of the other form.
Understanding keto-enol tautomerism may seem challenging at first, but it’s an important concept to grasp when studying organic chemistry. By understanding the interconversion between keto and enol forms, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how chemical reactions occur and how they can be manipulated for various applications. If you are looking for Solution: In which keto-enol tautomerism d… | Clutch Prep you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Images about Solution: In which keto-enol tautomerism d… | Clutch Prep like Keto Enol Tautomerism - What Is It and Why Is It Important?, Keto-Enol Tautomerism: Definition, Examples, and Mechanism and also Solution: In which keto-enol tautomerism d… | Clutch Prep. Here it is:
Solution: In Which Keto-enol Tautomerism D… | Clutch Prep
 www.clutchprep.comKeto-Enol Tautomerism: Definition, Examples, And Mechanism
www.clutchprep.comKeto-Enol Tautomerism: Definition, Examples, And Mechanism
 www.chemistrylearner.comenol tautomerism
www.chemistrylearner.comenol tautomerism
Keto-Enol Tautomerism: Definition, Examples, And Mechanism
 www.chemistrylearner.comenol keto tautomerism
www.chemistrylearner.comenol keto tautomerism
Keto-Enol Tautomerism: Definition, Examples, And Mechanism
 www.chemistrylearner.comenol tautomerism mechanism
www.chemistrylearner.comenol tautomerism mechanism
Keto Enol Tautomerism - What Is It And Why Is It Important?
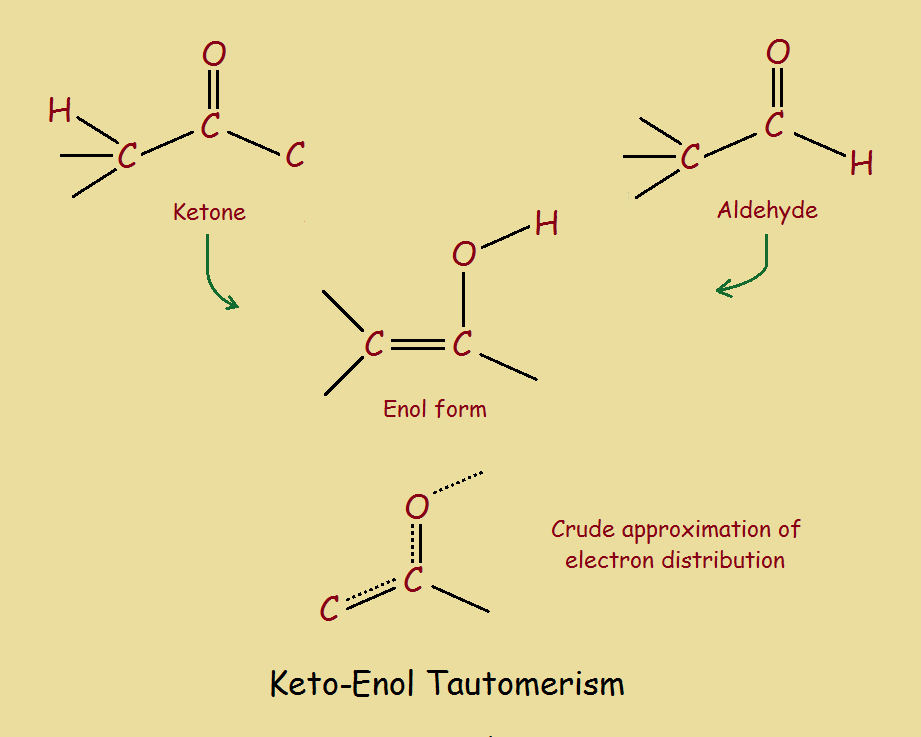 www.quirkyscience.comenol keto tautomerism chemistry xef4 quirkyscience ensuing attention
www.quirkyscience.comenol keto tautomerism chemistry xef4 quirkyscience ensuing attention
Solution: in which keto-enol tautomerism d…. Keto-enol tautomerism: definition, examples, and mechanism. Enol tautomerism mechanism